The current global industrial landscape is characterized by rapid technological advancements, increasing globalization, and a heightened emphasis on sustainability and efficiency. The core of this transformation is the integration of digital technology into all areas of business, leading to what is often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0. This revolution is marked by the emergence of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and advanced analytics, all of which are reshaping industries around the world.
One of the most significant developments in this landscape is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). IIoT refers to the extension and use of the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial sectors and applications. With a strong focus on machine-to-machine communication, big data, and machine learning, IIoT enables industries to improve efficiency, enhance productivity, and foster industrial growth. The IIoT encompasses a wide range of equipment, including sensors, devices, machinery, and technologies that are interconnected and communicate with each other.
The global Industrial IoT market is projected to grow significantly, reaching US$325.80 billion by 2024. This growth is anticipated to continue at a 12.68% CAGR from 2024 to 2028, leading to a market value of US$525.20 billion by 2028. The United States is expected to be a major contributor, with projected revenues of US$76.61 billion by 2024. This market expansion is largely driven by the rapid adoption of smart manufacturing technologies worldwide, which are transforming industrial operations and enhancing productivity.
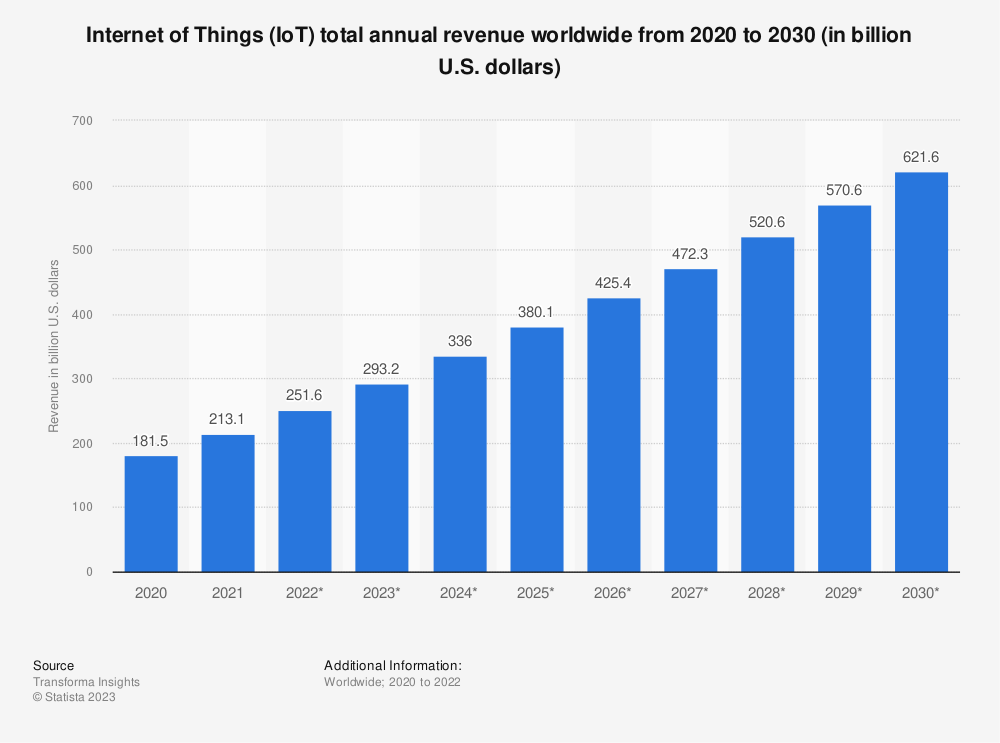
The total Internet of Things (IoT) market worldwide was worth around 182 billion U.S. dollars in 2020, and is forecast to rise to more than 621 billion U.S. dollars in 2030, tripling its revenue in ten years. Not only this, but the number of IoT connected devices worldwide is forecast to triple during this span in time.
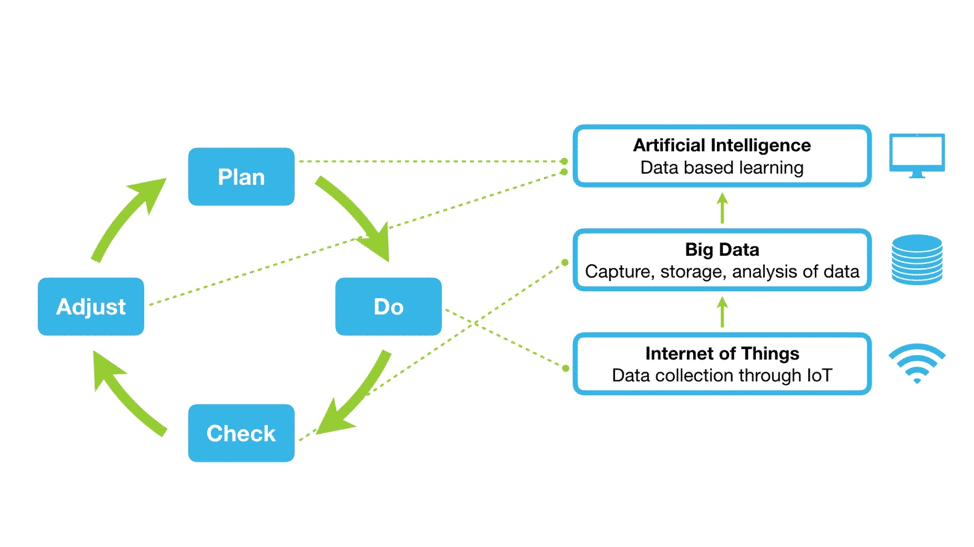
The significance of IIoT in optimizing industrial processes cannot be overstated. It allows for the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling industries to detect inefficiencies and problems sooner and react more quickly. For example, in manufacturing, IIoT can lead to smarter production processes by optimizing the supply chain, reducing downtime, and enhancing the quality of products. Predictive maintenance, a key application of IIoT, uses sensors and machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur, thus reducing maintenance costs and increasing equipment uptime.
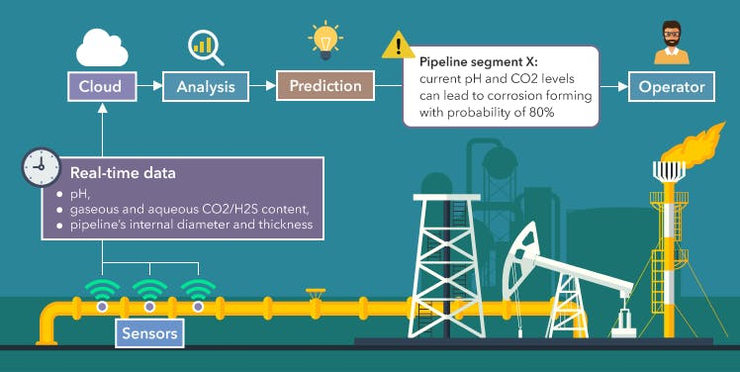
IIoT also plays a critical role in worker safety by monitoring working conditions and alerting about hazardous situations. In agriculture, IIoT technologies enable precision farming, which improves crop yields and reduces waste.
In the energy sector, IIoT technologies help in monitoring and managing energy consumption in real-time, leading to significant energy savings and reduced environmental impact. The transportation and logistics industry benefits from IIoT through improved fleet management, tracking, and route optimization, leading to faster and more efficient delivery systems.
Sri Lanka is rapidly emerging as a key player in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) arena, driven by its highly skilled workforce and robust university system. The nation is advancing in IoT and automation solutions, serving a diverse range of global clients, including Fortune 500 companies. Its expertise spans a wide array of cutting-edge technological services such as Data Annotation, Big Data Analysis, AI Solutions, and Predictive Analysis Models. Furthermore, Sri Lankan firms are adept in offering comprehensive technology consulting and engineering services, encompassing Enterprise Software Applications, Data Science, Embedded Systems, Remote Monitoring & IoT, Machine Learning, and Robotics. This innovative spirit is showcased in their dedication to developing Proofs of Concept for emerging technologies, emphasizing quality, tailor-made solutions, and exceptional service.
In parallel, the broader IoT landscape in Sri Lanka is witnessing a rapid transformation, primarily due to increased automation in key sectors like manufacturing and agriculture. The advent of 5G technology is revolutionizing connectivity, creating opportunities in education, healthcare, and financial services. AI applications are increasingly being adopted, enhancing business intelligence and decision-making. Crucially, IoT is transforming data collection, facilitating real-time monitoring and analysis in various industries. This holistic approach to embracing IoT is cementing Sri Lanka’s position as a leader in digital innovation in the region.
Industrial remote monitoring is becoming increasingly crucial in enhancing operational efficiency across various industries. This technology allows for continuous oversight of processes and equipment, even in the most remote locations, without the need for physical presence, thereby reducing the cost and logistical challenges of on-site management. Key benefits include improvements in operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced safety. It also leads to better quality control and environmental stewardship due to fewer emissions from reduced travel.
In manufacturing, remote monitoring enables real-time insights into production processes and supports predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For instance, OTIS Elevator uses advanced tools to foresee equipment issues, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling. In environmental monitoring, remote systems equipped with sensors can track emissions, helping industries comply with stringent regulations and mitigate environmental impacts.
The ThingsNode product stands out in the IoT landscape as a versatile and efficient solution for industrial data visualization and management. It boasts easy-to-use, plug-and-play devices that facilitate the creation of highly customizable dashboards. These dashboards can display real-time data, alerts, alarms, and allow for KPI calculation, amongst other functionalities.

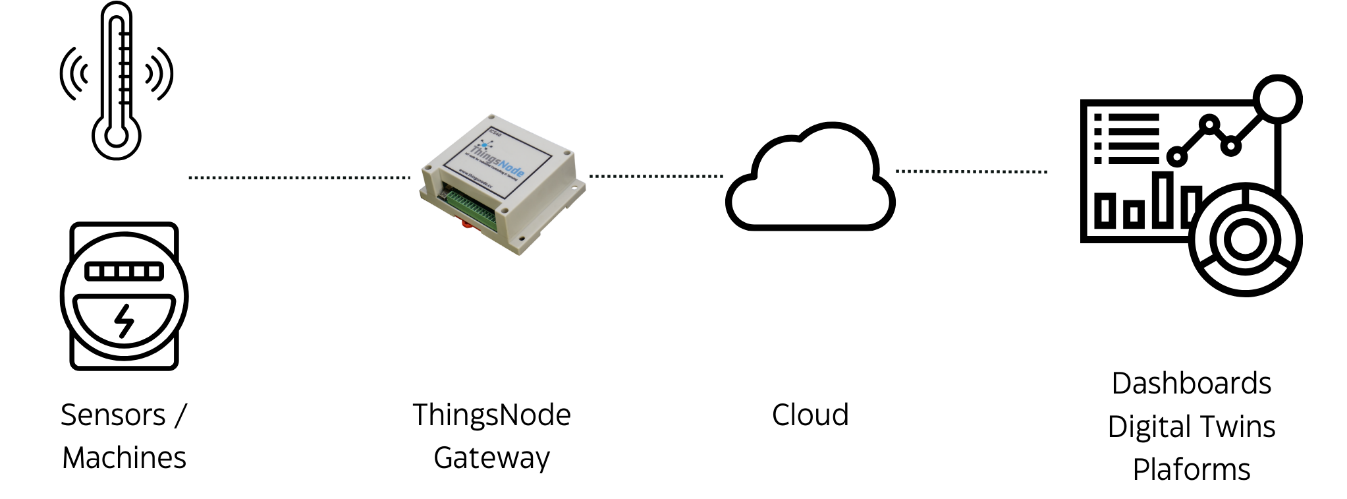 Notably vendor and platform-independent, ThingsNode can seamlessly connect to various clouds or ERP systems as well as with existing PLCs effortlessly. Its capability to integrate multiple sensors or devices makes it a flexible option for diverse industrial requirements. The product supports a range of communication modes including WiFi, 2G, 4G, and LoRa, ensuring broad connectivity options.
Notably vendor and platform-independent, ThingsNode can seamlessly connect to various clouds or ERP systems as well as with existing PLCs effortlessly. Its capability to integrate multiple sensors or devices makes it a flexible option for diverse industrial requirements. The product supports a range of communication modes including WiFi, 2G, 4G, and LoRa, ensuring broad connectivity options.
With user-friendly, easily configurable firmware, the product ensures that it can adapt to different industrial environments and needs. Furthermore, it is a cost-effective solution, providing two models of hardware that are packed with features, allowing selection based on specific solution requirements. The promise of over-the-air updates simplifies maintenance and ensures that the system can evolve with changing technological demands.
The following facts highlight specific features of Thindsnode and provide reasons for why you should choose it.
ThinsgNode Key Features:
- 3 Digital I/O
- Modbus Interface
- 2 Relay outputs
- Inbuilt Wifi
- Support for 2G/4G/LoRA
- Inbuilt Bluetooth
- 5-24V Power Supply
- Configuration tool
- Remote firmware upgrade
Reasons to Choose ThingsNode:
- Versatile functionality for multiple purposes
- Cost-effective solution
- Diverse communication modes
- Vendor-neutral compatibility
- Adherence to standard protocols
- Simplified configuration process
- Proven track record with 4 years in operation
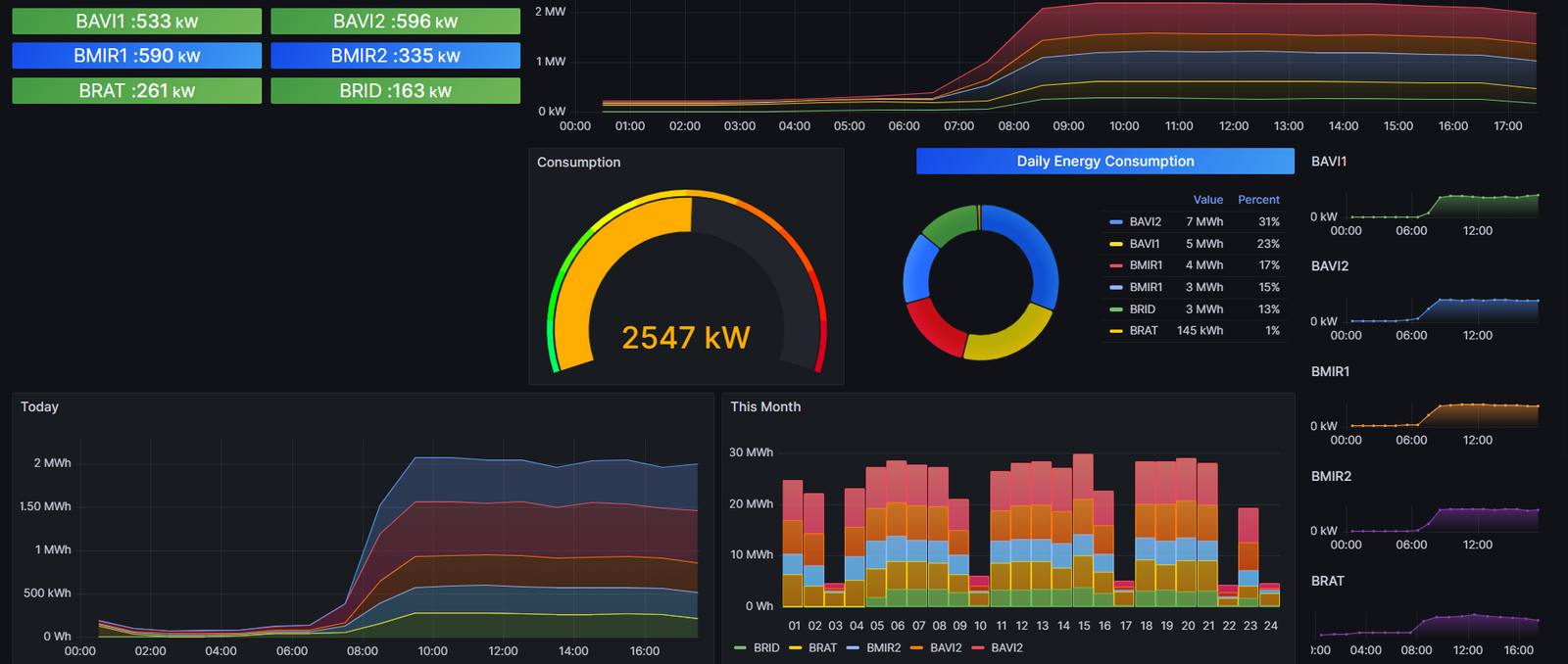 ThingsNode is at the forefront of ushering traditional industries into the era of smart industry. By leveraging ThingsNode’s technology, businesses gain real-time operational visibility, allowing for more informed and rapid decision-making. This heightened level of operational intelligence facilitates cost optimization, eliminating unnecessary expenditures through more efficient resource management. Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) becomes streamlined, empowering companies to track their progress towards operational excellence continuously. Furthermore, ThingsNode aids in identifying data patterns, unveiling opportunities for process improvement and innovation. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in helping industries meet their sustainability goals by enabling smarter use of energy and resources, thereby reducing the overall environmental footprint.
ThingsNode is at the forefront of ushering traditional industries into the era of smart industry. By leveraging ThingsNode’s technology, businesses gain real-time operational visibility, allowing for more informed and rapid decision-making. This heightened level of operational intelligence facilitates cost optimization, eliminating unnecessary expenditures through more efficient resource management. Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) becomes streamlined, empowering companies to track their progress towards operational excellence continuously. Furthermore, ThingsNode aids in identifying data patterns, unveiling opportunities for process improvement and innovation. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in helping industries meet their sustainability goals by enabling smarter use of energy and resources, thereby reducing the overall environmental footprint.
- Energy Efficiency: Real-time monitoring and control of energy usage can significantly reduce waste, allowing industries to operate more sustainably by conserving energy.
- Resource Management: ThingsNode can help manage resources more effectively, such as by optimizing water usage in agriculture through precision irrigation, which conserves water and reduces runoff pollution.
- Waste Reduction: By identifying inefficiencies and optimizing processes, ThingsNode can contribute to reducing industrial waste production.
4.Emission Monitoring: ThingsNode’s ability to monitor emissions can help industries in their efforts to minimize their carbon footprint and adhere to environmental regulations.
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing data to predict when machinery needs maintenance can extend the lifespan of industrial equipment, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental impact.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Improved visibility and data analysis can lead to more efficient supply chains, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and logistics.
- Sustainable Agriculture: For the agriculture sector, ThingsNode can enable sustainable practices by monitoring soil health, crop conditions, and optimizing the use of fertilizers and pesticides.
By integrating ThingsNode into their operations, industries can not only increase their operational efficiency but also support a more sustainable approach to business that aligns with global environmental objectives. In essence, ThingsNode is a transformative force for industries looking to modernize, optimize, and thrive in a connected, data-driven world.
The implementation of Thingsnodes will demonstrate how both local and global companies, considered the most trusted and popular, utilize these devices to achieve their goals and address challenges effectively
